As we all know, centralized exchanges are very risky. The history showed us, more than once, the potential risk which stems from many hacks happening over the last few years. Do you remember Mt. Gox hack? Or Bitfinex? Or maybe Bitstamp? Yea, many hacks happened, and many will continue to happen.
The whole idea behind blockchain is to avoid centralization and to introduce decentralization via technology. And then, we trade those decentralized assets in a centralized place? That doesn’t make any sense and isn’t logical. It is so wrong to save decentralized assets on a centralized place during such a crucial process as trading.
Crypto community realized this issue, and started working on a decentralized exchange. Today, we have a few of them in production and a few of them in R&D phase. In this article, we will try to make an overview of what’s going on with the development of these solutions and what we can expect from them.
How do we trade our decentralized assets?
Today, when someone wants to buy some crypto asset, firstly he has to buy one kind of asset with his fiat currency. It can be Bitcoin, Ether, Ripple or some other asset that you can buy with the dollar, euro, etc. For example, you transfer the money from your bank account to Coinbase, Bitstamp, Kraken or some other crypto exchange that works with fiat currencies. After that, you have to buy Bitcoin, Ether or other asset to be able to buy some other asset in pairs btc/(asset) or eth/(asset). But, do you know where you put your money? It does not belong to you anymore since you gave it to centralized exchange, now your money is in their hands. If we go back to 2009 when Satoshi released Bitcoin whitepaper, we will see that this process goes against the goal that Bitcoin aims to reach.
Most exchanges now have Know your customer (KYC) policy, so to start trading you have to send your ID document to them. Of course, only if you are lucky and the exchange didn’t close new registrations, like many of them did. When you register on some exchange, you mostly have to wait at least a few days to get approved by the support team, sometimes even a few weeks. Unfortunately, problems don’t stop once you are in, centralized exchanges have been known to reduce withdrawal limits without warning so you can end up with valuable assets which you can withdraw only in small amounts. Besides that, they sometimes suffer from unscheduled downtime or experience other technical difficulties, and you can’t do anything about it.
Centralized exchanges sometimes act like a dictator or government, demanding high prices to get a coin listed or delist a coin because of some arbitrary reason. Also, sometimes you can’t withdraw assets because the wallet for a specific currency is being updated.
Why would I transfer my money from one centralized institution (banks) to another (crypto exchange)? And why would I hold my bitcoins there? All those exchanges are centralized, which means that I just transfer my funds from one hand to another, but I still don’t have full control over them. Of course, we can move our funds to our private wallet, but the fact that we have to make every trade without having full control of our funds is just ridiculous.
You don’t own your assets in centralized exchange
When you log in to your centralized exchange account, you can see your assets balance. You think you have your wallet with them? Wrong! That amount of BTC or some other asset that you can see, is not actually yours. Centralized exchanges are all about database management, you don’t hold any cryptocurrency. You just have a number beside your name in the database, and you can trade with that number.
That way exchange can process many orders efficiently. But, only when you withdraw crypto from centralized exchange to your private wallet, on which you have the private key, you have full control over it. This trading system requires having a lot of trust in third-party exchange, but most people don’t even trust their government or financial institutions, and now we have to trust some web service.
Just imagine, if government decides to ban crypto and conclude that all exchanges in the country are doing illegal operations. Government could freeze all their funds, a company would not be able to touch them anymore, so you would lose your funds as well. You weren’t guilty of anything. In this market where we don’t have any regulations that scenario is still possible. Long story short, the centralized exchange is the main reason of failure with crypto. It’s far away from the initial goal of a crypto ecosystem which should provide freedom from central entities.
What is a decentralized exchange?
A decentralized exchange is an exchange that does not rely on a third party service to hold user funds. The whole idea is that trading takes place directly between users, in a real peer to peer mode.
That way, the user would have full control over his funds, and he is entirely responsible if something happens. Hackers would not be able to hack into the exchange and take user funds, so trading through a decentralized exchange would be more secure and safe.
Existing work on this topic
Most decentralized exchanges are built on Ethereum blockchain, but we are not impressed with their progress. Ethereum smart contracts failed to generate significant trading volume due to their inefficient design for this purpose. Every fully decentralized exchange on this blockchain is expensive for someone who wants to trade. To be clear, it’s not expensive to make a single trade, but it’s expensive to modify order all the time depending on volatility of the market. Whenever someone modifies an order, it must be executed on smart contract and user will spend gas for that action. If user makes a few modifications and then closes the order, he will lose gas even though he didn’t make any trade.
That is the problem; it’s hard to trade in this evolving market conditions without frequently modifying orders in response to them. On top of that, since everything should be executed on the blockchain, trading consumes network bandwidth without resulting in value transfer. Some orders will result in value transfer, but there will be many more actions, like editing and canceling orders, that won’t.
Of course, that is only one approach; another alternative is using automated market maker (AMM) smart contracts.
The AMM smart contract replaces the order book with a price-adjustment model in which an asset’s spot price deterministically responds to market forces and market participants on either side of the market trade with the AMM rather than with each other. Read more at 0x whitepaper.
Although this approach makes trading always available, it has some imperfections. For example, the price for which you can sell/buy can be worse than your desired price. AMM has price-adjustment models that make trading insensitive to market liquidity. It means that trades can cause prices to move up or down according to market forces.
AMM approach is not ideal, so state channels are introduced to help scale Ethereum blockchain and reduce costs for a variety of applications on it, including exchanges. In this approach, transactions are moved off the blockchain, and any edits are made off the chain. When everything is known, the transaction will be executed on the blockchain. All sides in a state channel must pass cryptographically signed messages back and forth, accumulating intermediate state changes without publishing them to the blockchain. Channel will publish them on blockchain only when it is closed. This approach is ideal for applications where many intermediate state changes may be accumulated off-chain before being executed as a transaction on the blockchain. To get a bigger picture, we are talking about use cases like poker, day trading, turn-based games etc.
With state channels, if one participant leaves the channel or attempts to cheat, there is a challenging period of time during which one participant can send to the blockchain the last message he received from the other participant. Unfortunately, this means that both participants have to be online to agree on the trade. This approach drastically reduces the number of blockchain transactions, but it’s not cheap to open and safely close the state channel. So it’s not efficient to use this kind of service just for one-time transactions.
Motivated with state channels, some of them took a new approach that is based on the off-chain relay. This design is using broadcast, so in this approach participants that want to make an order will send it off-chain where anyone can pick it up and pass it to a smart contract for execution. With this approach only a few on-chain transactions are required to perform a trade, but still, it suffers from performance issues in comparison to centralized exchange. Also, because order matching is not automatic, there is an arbitrage risk for users who don’t manage to cancel their order in time.
Liquidity is a big challenge here
Unfortunately, problems with performance and cost are not the only one; liquidity is also a big challenge with decentralized exchanges. They still lack the commodity, ease of use and user support to be able to attract mainstream users as Coinbase did. Because of that, there is no as much capital in circulation so when someone wants to execute a significant order it’s quite possible that it won’t be fully executed, probably only a part of tokens will be sold/bought.
If they improve the liquidity that would be a great first step to encourage mainstream adoption and to get more users on it. Many factors contribute to the liquidity of an asset, but if the way in which consumers make transactions could be simplified, then we can just imagine how fast the demand for such assets would increase.
Projects working on those problems
NEX
In contrast to these approaches, recently NEX joined the game. That project aims to surpass all those problems with their system design, with which they would potentially retain all performance of centralized exchange and security of decentralized exchange. Also, they don’t want to use Ethereum blockchain; it’s the first decentralized exchange built on NEO blockchain. Personally, I like their approach, but we should be aware that they will have one system component (mapping one) that will be off-chain and will be centralized. What does it mean? If someone creates an order, the centralized part will have access to their funds but only those included in that specific trade. It’s still a trade-off between safety and performance.
WavesDEX
WavesDex is a decentralized exchange built on Waves blockchain where users have full control of their funds, but a matching mechanism is centralized like it’s the case with NEX. On this exchange, users can trade cryptocurrencies for Waves token of any other asset token issued on the Waves platform.
According to their blog post, orders are paired on centralized basis by matcher nodes. Those nodes execute a trade but have no access to user funds, when matching is done they settle the trade on the blockchain for maximum security. In short, all orders are sent to the centralized server which matches them at high speed, but an actual valuable transfer of funds executes on the waves blockchain.
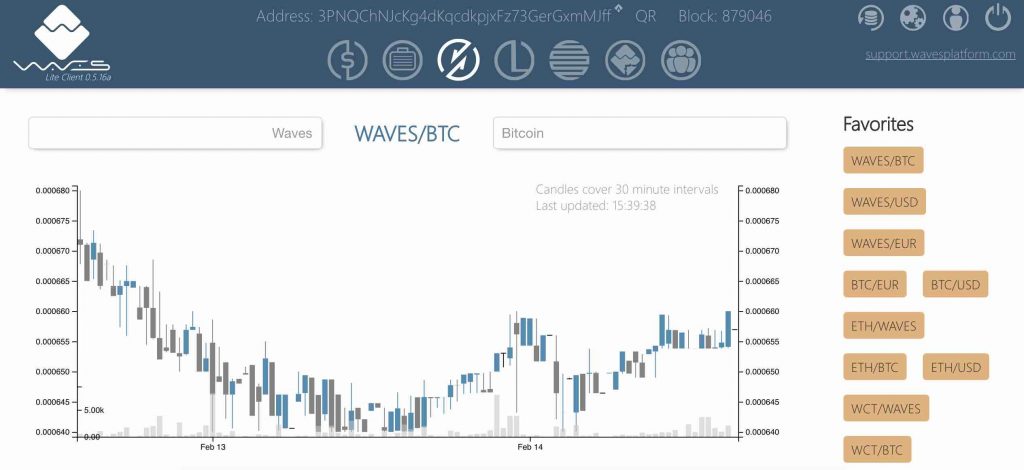
In the time of writing this article, according to coinmakercap, Waves Dex trading volume in the last 24h is around $700k, that is pretty high for decentralized exchange.
Bisq
This open source desktop application enables users to trade Bitcoin for other altcoins or national currencies. It has some similarities to LocalBitcoins, but it works slightly different. On both platforms, user has to find another user with whom he will make a trade. With Bisq, there is no need for registration, no single point of failure and it’s completely private.
They also have some other cool features, such as the fact that it does not hold user funds. Bisq uses decentralized arbitration tools and security deposits to protect traders at all times. Also, communication through Bisq is end-to-end encrypted over the Tor protocol. Approach with Tor protocol is something that users will appreciate.
According to their blog post, Bisq significant benefit in comparison to others is the fact that you can exchange bitcoin-to-fiat in a decentralized way. Take a look at some features and descriptions that you can find on their website:
- Bisq does not hold any bitcoins. All are held in multisignature addresses rather than a Bisq-controlled wallet.
- Bisq does not hold any national currency. The national currency is transferred directly from one trader to the other.
- Bisq uses a Peer-to-Peer network over Tor. This means there are no servers to be hacked or DDoS’d.
- Bisq does not know the traders. No data is stored on who trades with whom.
- Bisq does not require registration. This means privacy is maintained, there are no “approval” wait times, and identity theft becomes impossible.
- Bisq is not a company. It is an open source project organized as a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO).
Also, as we said before, you can exchange bitcoins for fiat currency. Take a look at supported payment methods:
- SEPA
- Zelle (formerly known as clearXchange)
- Faster Payments
- National bank transfer
- Swish
- Chase QuickPay
- Interac e-Transfer
- Western Union
- US Postal Money Order
- Cash Deposit
- OKPay
- Perfect Money
- Alipay
- Transfer with the same bank
- Transfer with specific banks
At this moment, they accept 60 different cryptocurrencies and tokens, but they still don’t provide significant trading volume.
According to the coinmarketcap, they only had a $10k trading volume in the last 24h. With this application there is one big problem, when you publish your order you need to stay online so it can react when another trader wants to take your offer. MulstiSig deposit transaction they are using is created in the take-offer process, so you have to stay online to complete the trade. If you shut down the application, your offer will be removed from distribution offer book and other users won’t see it available. When you start Bisq application again, your offer will be re-published.
Besides that, users can’t edit created offer once it’s published. You can use the percentage based price so your price will modify according to the market price. For example, if you set buy order with percentage price to 5% below the market price, your buy order will be updated with every market price update (every 90 sec).
Stellar DEX
We all know Stellar because it is one of the top 10 cryptocurrencies according to coinmarketcap, but what most of us don’t know is the fact that the team behind Stellar made the functional decentralized exchange. They want to support the issuing and movement of assets, so the Stellar network acts as a decentralized exchange of any asset that people have added to it. Every account can make an offer to buy or sell some asset using the manager offer function. Only accounts that have specific asset can make an offer with it. The offer is checked against the existing order book for that asset pair (for example XLM/BTC), and if offer crosses with some other offer, it’s filled and executed.
An order book is a record of created orders on the Stellar network, so all offers selling BTC for XML are listed there and also all orders selling XML for BTC. When some of them matched, an order will be executed.
Also, it’s good to mention, on this decentralized exchange it is possible to execute cross-asset payments with assets that you don’t have. For example, if you want to trade XML/BTC but you don’t have XML, you can trade ETH/XML/BTC. In short, the exchange will transfer your ETH to XML to make a desired trade.
In comparison to exchanges mentioned above, Stellar DEX has better liquidity, at the time of writing this article it has a $2.8M trading volume in the last 24 hours.
Ether Delta
This exchange is probably the most famous decentralized exchange since it’s straightforward for ERC20 ICO-s to list their tokens. Ether delta is cryptocurrency exchange build specifically for ERC20 tokens and Ethereum pairs. This exchange is different because it runs on Ethereum smart contracts that are responsible for everything, including managing trading, deposits, withdrawals and wallet integration.
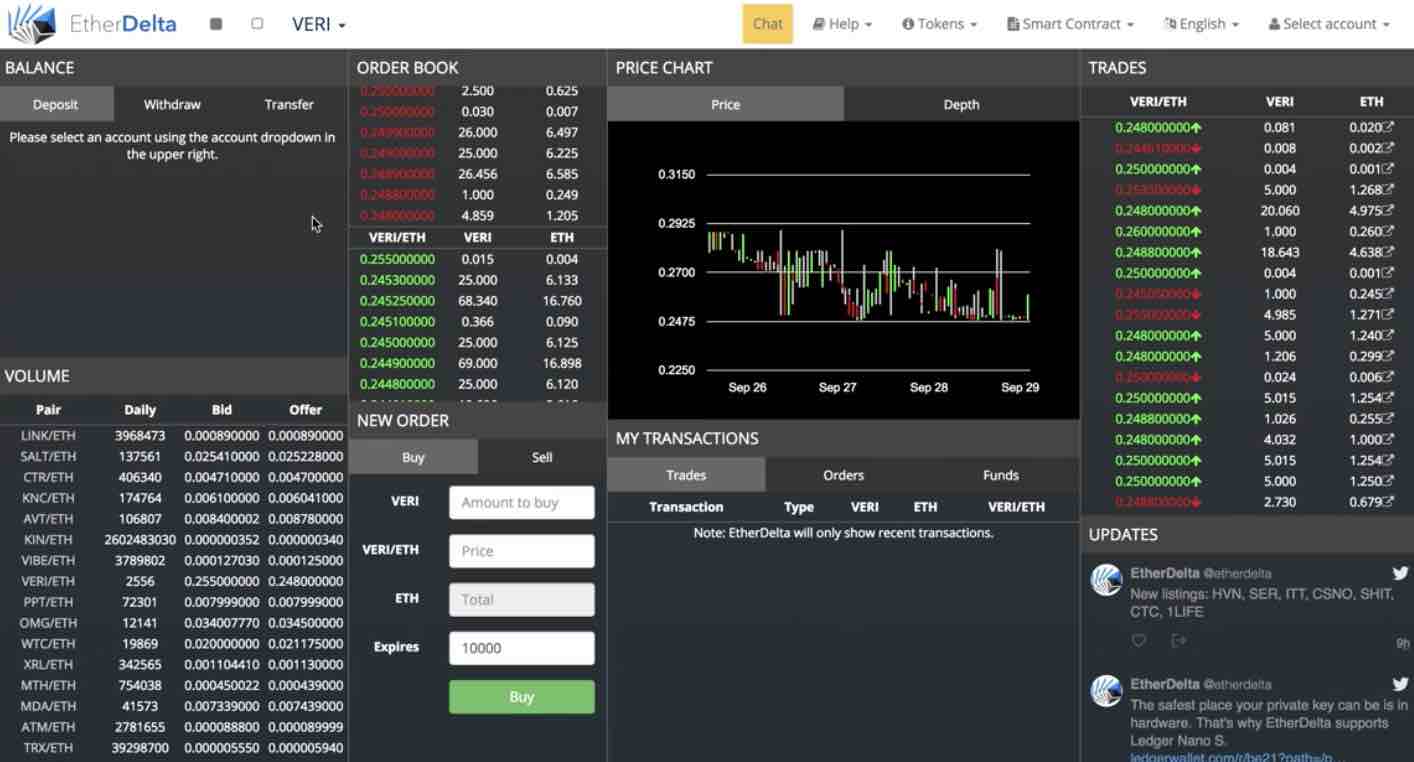
Unfortunately, this exchange is not so user-friendly, and for most general investors it’s really hard to use it. The interface looks so unsophisticated in comparison with more user-friendly exchanges like Coinbase, Bittrex, Bitstamp, etc. But, of course, that’s just the first impression, when the user gets familiar with it, it’s easy to use. The problem is that people don’t want to wait, and many of them probably don’t care about security and decentralization, they just want to use something intuitive.
Ether delta works like one big smart contract, and most of the exchange functions are realized through it. Also, it’s anonymous; you don’t have to open an account like you have to on the centralized exchange. You can manage all your funds directly using your own Ethereum wallet address. You have two options, you can either import you old Ethereum wallet, or you can create a new one with the exchange. The best thing is that you can sync a Ledger Nano S or Meta mask account to it.
You can’t trade directly from your Ethereum wallet, to use Ether Delta you have to transfer funds from your personal Ethereum wallet to your Ether Delta wallet. Maybe this is a big concern to you, but you should be aware that the decentralized nature of Ether Delta make it one of the most secure exchanges out there. With Ether Delta all your funds are managed outside of the exchange. Because of that, hack on Ether Delta didn’t happen on the exchange, it happened on the website and domain name so it was a phishing scam, but Ether Delta application was not hacked.
Ether Delta is a great exchange and it is decentralized in a way it should be, the problem is the learning curve which is steep. As we said before, it’s exchange only for ERC20 tokens, so it’s not so attractive to a new user because it’s the only exchange that doesn’t support the most popular cryptocurrency Bitcoin. Besides that, Ether Delta has acceptable liquidity, At the moment, in the last 24 hours it has around $2M trade volume. That is great but most of trading volume is made on just a few pairs, so many of them exist but without any liquidity.
Bitfinex?
We all know about Bitfinex cryptocurrency exchange, it has been here for a while. I think it was founded back in 2012, and today it’s one of the most liquid exchanges. It has more than a billion dollars trade volume every day. On February 2nd, 2018 they announced EOSfinex, a high-performance decentralized exchange built on EOS.IO platform.
According to their blog post, they continue to push the boundaries of market-leading services and will combine the scalability and speed of EOS.IO with Bitfinex’s industry-leading expertise to deliver a decentralized exchange designed to offer a fast, transparent and trustless platform for trading digital assets.
Bitfinex is one of the leading exchanges in the world, and they don’t want to be replaced with some decentralized exchange. They know what the future is and they adapt accordingly, if decentralized exchange is the future, they want to be a part of it.
Blocknet DEX
The blocknet decentralized exchange requires zero KYS, your coins are yours and in your possession at all times. You trade directly from your own wallet. Also, 100% of trading fees generated from exchanges on the protocol are distributed to the network service providers (staking and service node operators). That way, whether in a bull market or a bear market, exchanges will always make money, no matter what. However, in the case of Blocknet, it’s the service providers who will profit.
This exchange is built on the Blocknet protocol, and it uses atomic swaps via the Blocknet XBridge protocol. That way, a trustless, direct wallet to wallet exchange is achieved, and there is no need for a centralized third party of trust. Trades use a single hash which is shared between two parties, and two transactions on each chain take place using asynchronous timelock.
0x protocol
This is not DEX application, it is a piece of technology with which you can make your DEX. 0X is the exchange protocol implemented within an Ethereum smart contract that is publicly accessible and kind of free to use, you just have to spend gas for smart contract operations. A protocol is written in Solidity programming language and contains two simple functions: fill and cancel. It’s not a big contract, it has just around 100 lines of code.
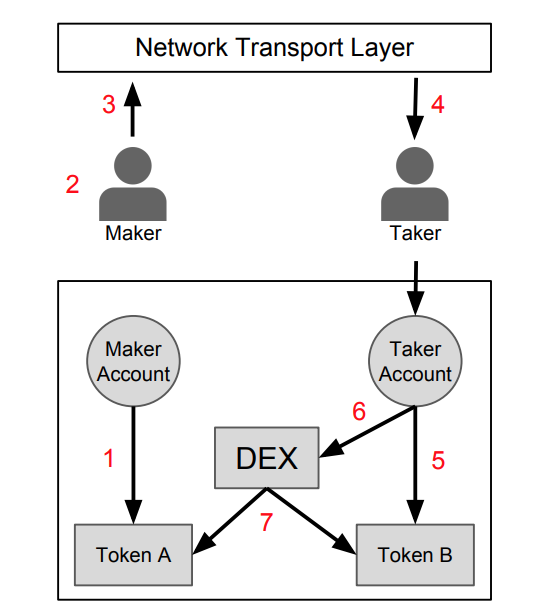
On the picture above, you can see the general design used to implement off-chain order relay and on-chain settlement, which is possible to achieve with a 0x protocol.
- The maker has to approve the DEX contract to access his balance of token A
- The maker has to create an order to exchange token A for token B and sign the order with private key
- The order should be broadcasted over communication layer
- The taker picks an order which he wants to execute
- The taker has to approve the DEX contract to access his balance of token B
- The taker submits signed order to the DEX contract
- DEX contract authenticates signatures, verifies order and then transfer tokens between the two parties
With 0X protocol, already a few dApps are launched, and also a few DEX applications, one of them is a ddex.io decentralized exchange.
Swap protocol
Swap is a protocol that helps to make a peer-to-peer ecosystem for trading ERC20 tokens on Ethereum blockchain. Their design supports efficient counterparty discovery, and negotiations, and they believe that only a few messages are enough to negotiate a trade between two users. It’s similar to 0x protocol, the maker and taker perform trade negotiation off-chain, and then taker will send an order to the contract to execute an order on the blockchain.
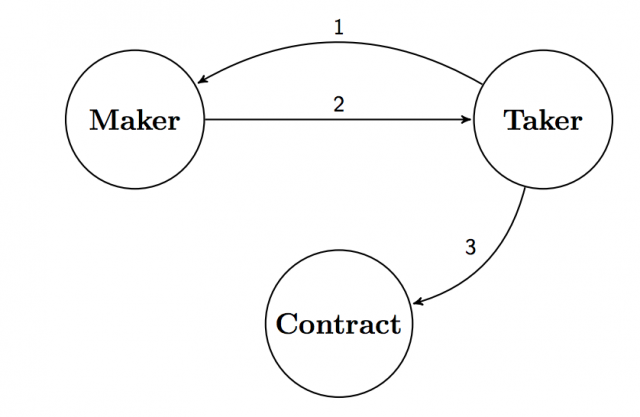
- The taker has to call getOrder on the maker
- The maker replies with an order
- The taker calls fillOrder(order) on the smart contract
In comparison to 0x protocol, swap is using P2P design and the team behind it believes P2P design is more efficient for blockchain trades and settlements than relayer design that 0x is using.
Conclusion
We are aware that centralized exchanges will become history sooner than expected, but decentralized exchanges have to update their technology to be attractive to the regular user. Otherwise, they will not be able to reach mass adoption. That means they have to make the trading process easy and straightforward for non IT user; also their user interface should be better. Today we have a few centralized exchanges in every country, and each of them has their own liquidity pool. If decentralized technology and protocols for exchanges success the design where whatever exchange you use you can match your order with orders from other exchanges, they will merge liquidity pools. When they do that, liquidity would not be a problem anymore.
